Communication Service Providers (CSPs) are increasingly dealing with more complex networks, especially with the introduction of 5G services. These operators will deal with these complexities by introducing network transformation programs to implement new technologies, securing networks, and automating the network. How much of these complexities will be dealt with by the CSPs or will it be outsourced to the Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
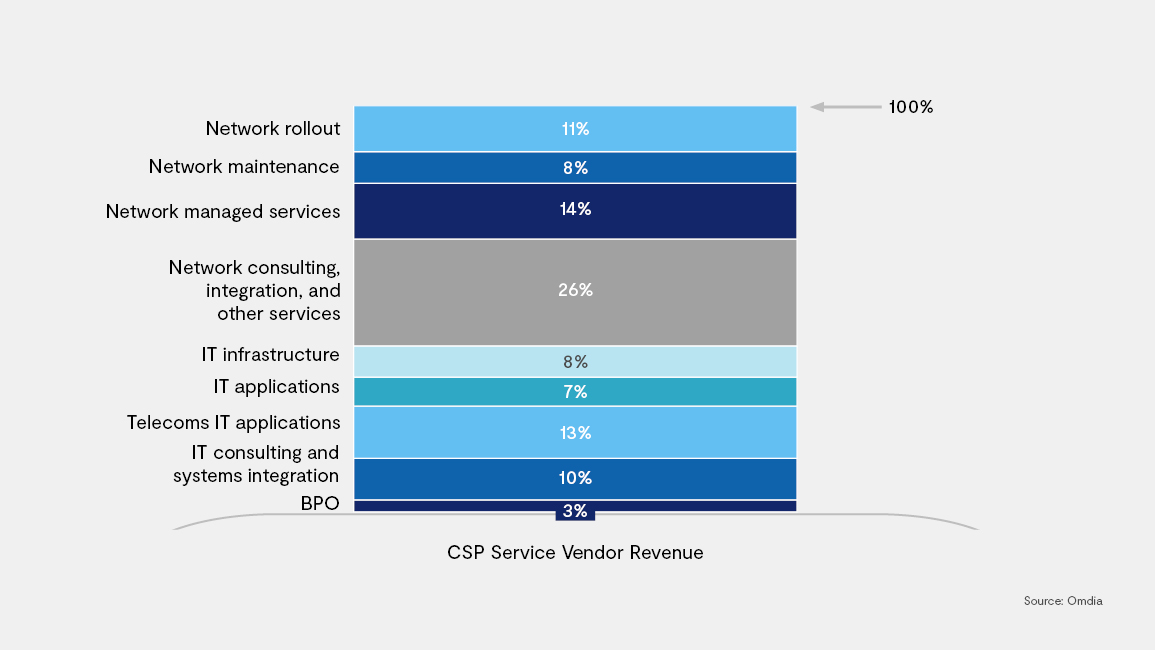
Managed Service Providers are still today playing a key role in the CSP’s network and CSP service vendors are claiming the biggest portion of the revenue market, in network managed services (14%), network consulting and integration services (26%) and for the network rollout and maintenance (19%) (Source: Omdia).
Managed Services (MS) are used by CSPs to improve their operations and customer experience, simplify their organization, and reduce costs. The demand for managed services is evolving, and MSPs need to respond to the demand and complexities of the transforming CSPs.
Participants wanted for Managed Services Survey!
In our new survey, we would like to identify how critical it is for a CSP to automate its network by an MSP.
>> We would like you to participate in our updated Managed Services Survey – click here
Over time MS have moved from simple out-tasking towards partnership models with appropriate commercial setups reflected in the pricing as well as KPI / SLA models. With the introduction of automation, the operators and their managed services/operations partners will meet new challenges such as decisions on investment, ownership of the automation systems and fair distribution of benefits between MSPs and MNOs.
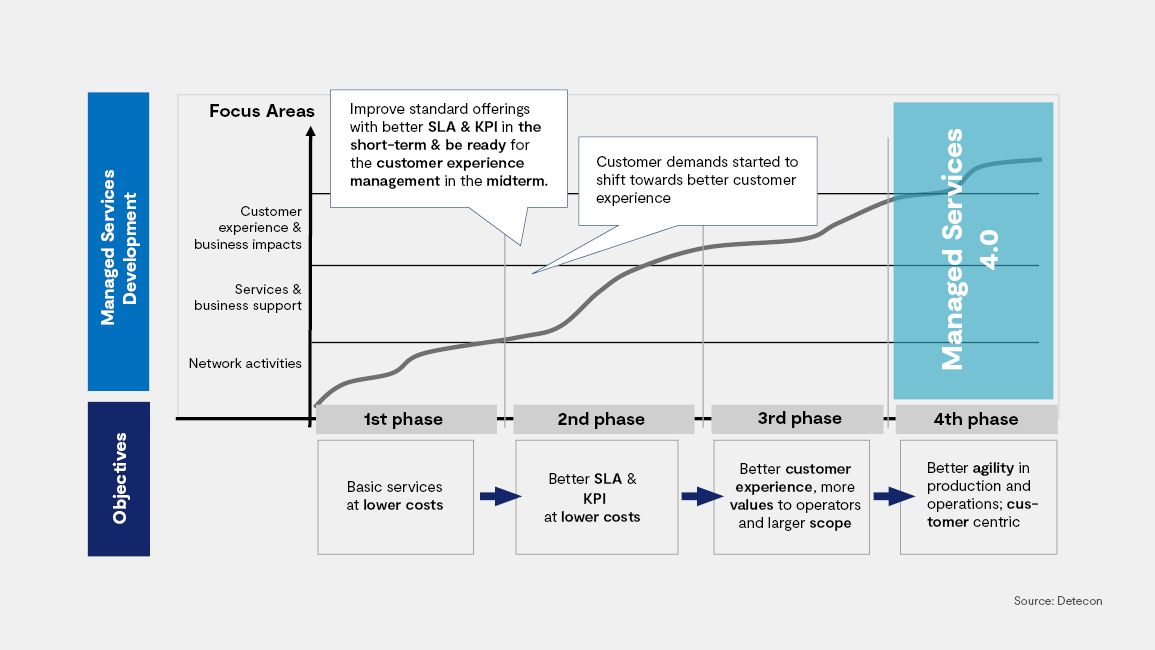
The survival of an MSPs and CSPs in 2030
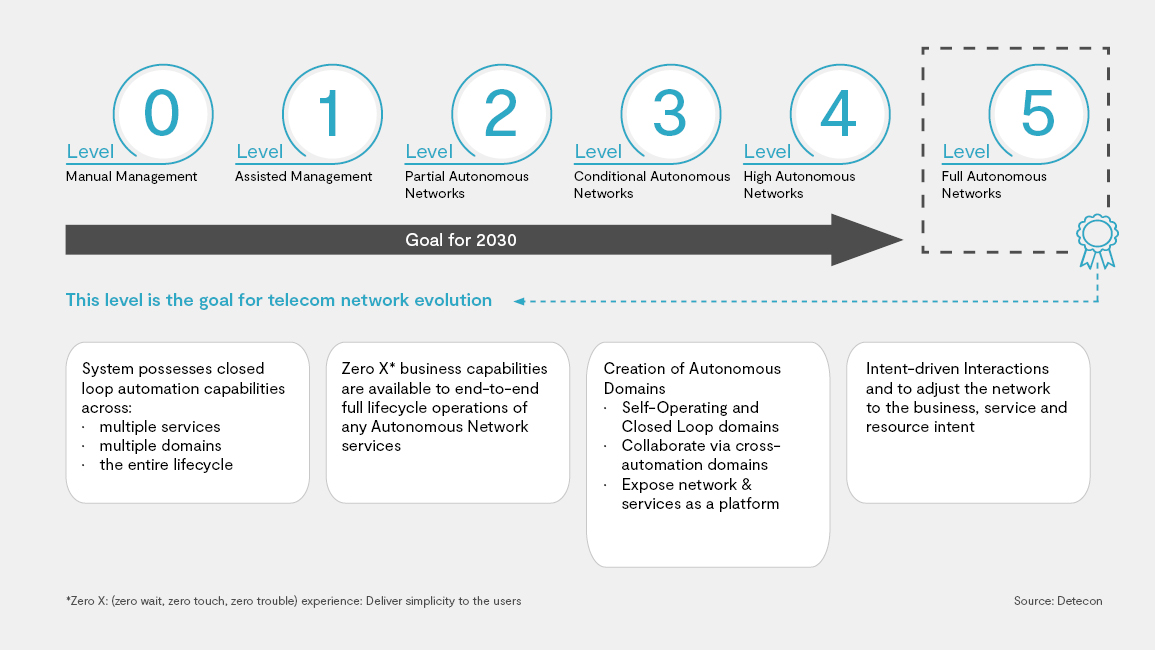
The goal for a CSP is to be a fully autonomous network at Level 5 (Source: TMForum) and this includes creating closed loop automation capabilities across multiple domains, services, and lifecycles, with Zero-X capabilities, and having intent-based interaction according to the business and resource intent.
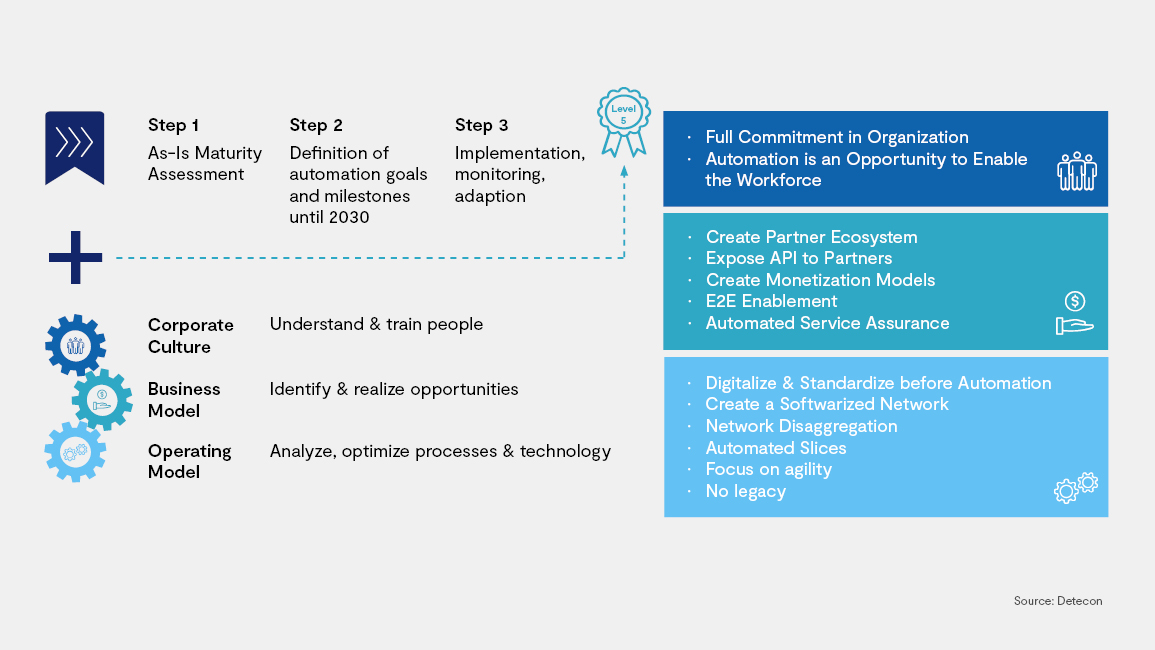
The Managed Service Provider of the future needs to be able to implement and support the level 5 automation capabilities in the CSP’s network and needs to adapt to the new operating models of the CSPs. For a CSP it means aligning its managed service strategy with that of it is automation strategy, to be part of the corporate culture, business models and operating models.
The MSP needs to support DevSecOps, Infrastructure as a Code, GitOps, AIOps and Site Reliability Engineering for Continuous Integration and Continues Delivery (CI/CD) with the right tools and systems in place. The MSP must implement and support this across multiple domains and across multiple vendors and suppliers, especially when networks are becoming more disaggregated with the introduction of OpenRAN and Fixed Access 4.0 (Source: Deutsche Telekom).
Based on our previous 2017 Managed Services Survey the top strategic focus areas for CSPs where to improve the service quality and customer experience, improve network coverage and capacity, and service deployment.
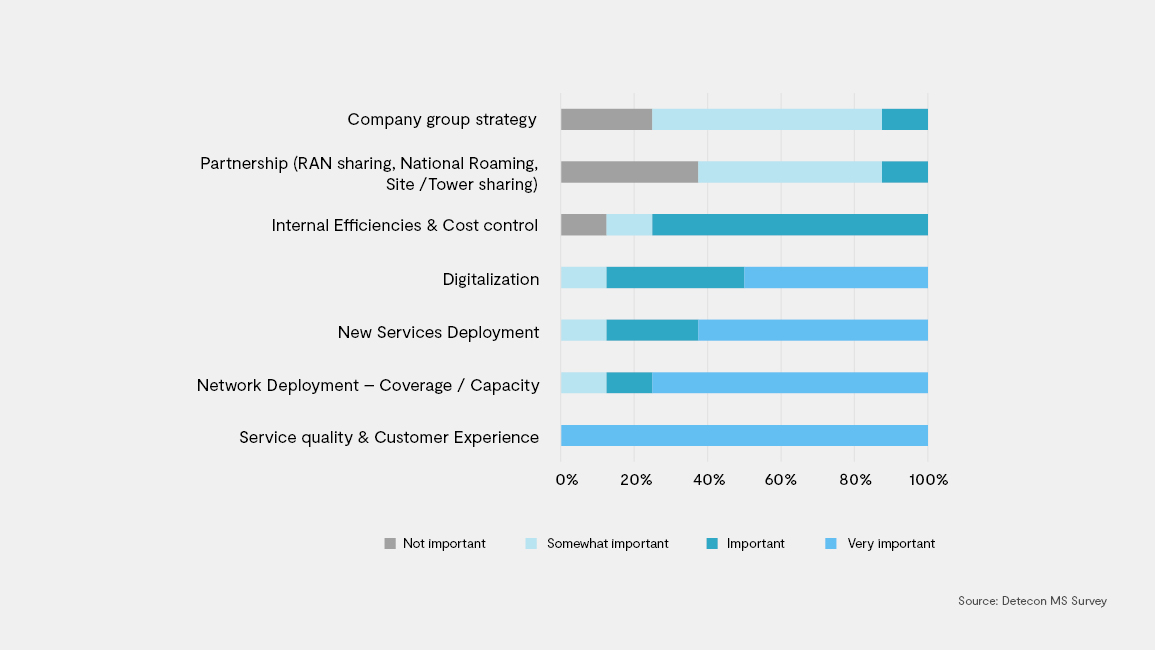
Internal efficiency and cost control were not among the top three topics and digitalization was new and becoming an important topic. With the technologies and operations transformation and the MS 4.0 evolution, this focus is shifting back to cost control, more efficiencies and insourcing / in-house development of key capabilities.
This is done by a high level of automation that is either done in-house by the CSP or by their external partners / Managed Service Providers in the business, service and network operations areas, that use automation effectively to achieve efficiency gains, improve productivity and reduce costs.







